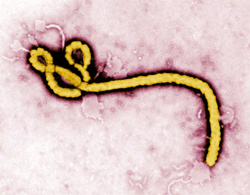
Ebola Viral Haemorrhagic Fever (VHF) in West Africa.
Healthcare professionals are particularly vulnerable as they assess and treat individuals. Could you spot Ebola and would you live to tell the tale?
| Microbiology Nuts & Bolts |
|
 Anyone watching the news today can’t help but notice the current outbreak of Ebola Viral Haemorrhagic Fever (VHF) in West Africa. Healthcare professionals are particularly vulnerable as they assess and treat individuals. Could you spot Ebola and would you live to tell the tale? I was phoned a few evenings ago by a very excited orthopaedic surgeon who was convinced he had clinically diagnosed a case of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) osteomyelitis. The patient had been living and working
in Sub-Saharan Africa for a year and had presented with a painful swelling of the distal end of his clavicle associated with a fever. A sample of pus had been aspirated from the bone by the radiologists and the surgeon wanted an urgent ZN stain for MTB. Mr Jones comes in to your clinic asking about antibiotic
prophylaxis for a dental procedure he is having next week. He had his aortic valve replaced 5 years ago and shortly afterwards he had some dental work done where he was given prophylactic antibiotics to stop his heart valve becoming infected. This time he has been told that he doesn’t need any antibiotics and yet he is having the same dental procedure done. He’s wondering why he needed antibiotics before and not now? What has changed? He’s very anxious and has come to you looking for guidance. Clostridium difficile Associated Disease (CDAD) is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium difficile. In order to acquire it the person has to ingest it, but where they ingest it from is not yet known. The more places scientists look for it, the more they find it, including in retail foods, animals, plants and various water sources. Antibiotics predispose to infection by eliminating the normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract and leaving an ecological niche for the C. difficile bacterium to exploit. The bacterium then produces a toxin which causes a colitis ranging from mild diarrhoea up to pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon and even death.
The most commonly implicated antibiotics are known as the “4Cs” and include: • Cephalosporins • Ciprofloxacin (and the other quinolones) • Clindamycin • Co-amoxiclav |
Facebook has deleted the Microbiology Nuts & Bolts pages - if you want your weekly dose of microbiology then you will need to come here, and we look forward to you continuing to read it!
Blog Author:
David Garner Please DO NOT advertise products and conferences on our website or blog
Categories
All
Archives
November 2022
Categories
All
|