Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM)
The majority of systemic antibiotics do not need to have their levels monitored. However, for others it is essential:
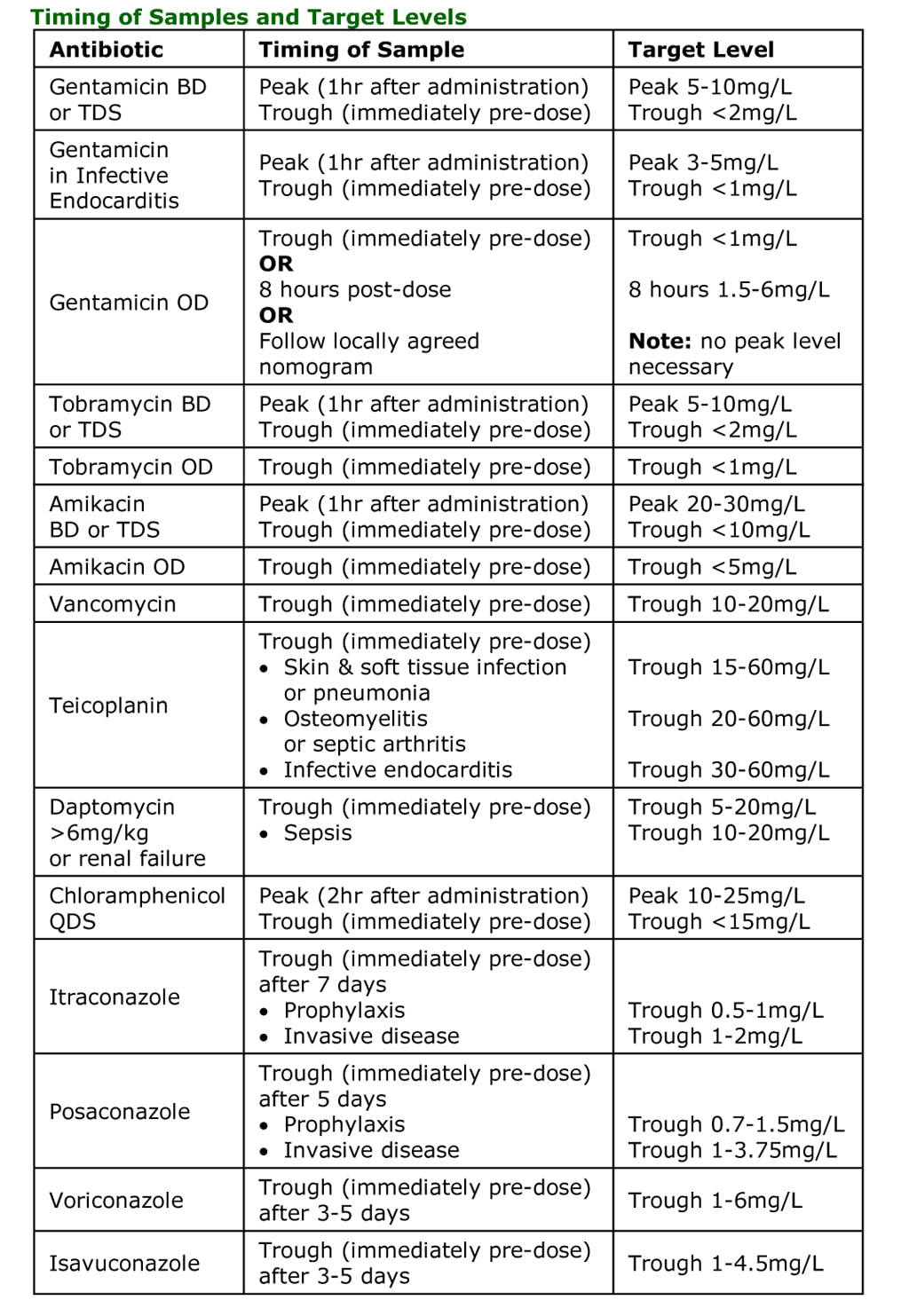
Antibiotic assays should be taken at the correct times, usually:
Serum samples should be sent at the time of the 3rd or 4th dose, approximately 2-4mls of blood = 1-2mls of serum, in red or yellow topped vacutainers. Subsequent levels should be checked twice weekly if renal function is stable or more frequently if renal function changes.
- Aminoglycosides - Gentamicin, Tobramycin, Amikacin
- Glycopeptides – Vancomycin, Teicoplanin (doses in excess of 400mg)
- Daptomycin (doses in excess of 6mg/kg or renal failure)
- Chloramphenicol (children under 4 years old, the elderly and those with hepatic impairment)
- Antifungals – Itraconazole, Posaconazole, Voriconazole, Isavuconazole
Antibiotic assays should be taken at the correct times, usually:
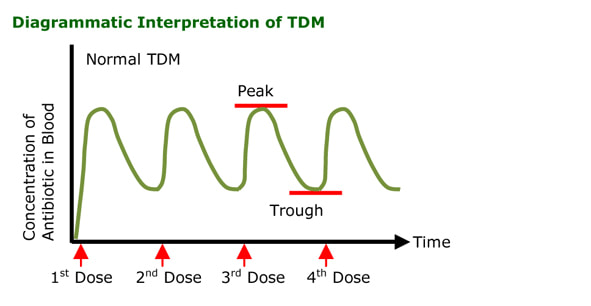
- Peak - 1 hour after administration
- Trough - immediately before administration of the next dose
Serum samples should be sent at the time of the 3rd or 4th dose, approximately 2-4mls of blood = 1-2mls of serum, in red or yellow topped vacutainers. Subsequent levels should be checked twice weekly if renal function is stable or more frequently if renal function changes.
Gentamicin, Tobramycin and Amikacin
- Peak level (post-dose) generally assesses whether a therapeutic level has been achieved, therefore levels not required for once daily dosing
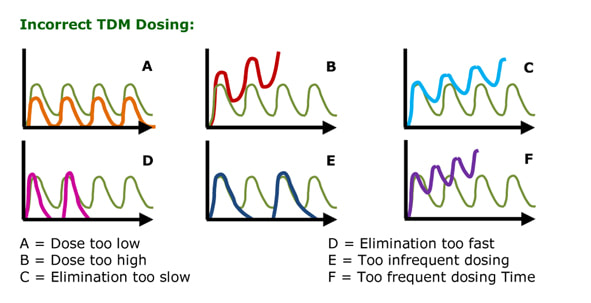
- If peak too high: dose too high therefore reduce dose by approximately 10% (Graph B, Diagrammatic Interpretation of TDM)
- Trough level (pre-dose) generally assesses whether toxic levels are accumulating
- In severe renal failure check levels daily and redose when target level achieved
Vancomycin
In order to interpret Vancomycin TDM, the dosing regimen must be followed accurately otherwise the result cannot be interpreted.
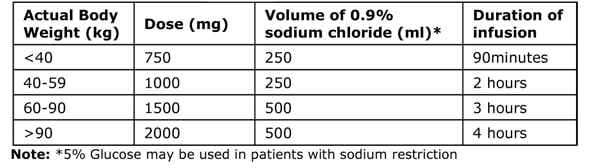
Dosing Regimen Step 1: Give a Loading Dose
This is based on Actual Body Weight
Dosing Regimen Step 1: Give a Loading Dose
This is based on Actual Body Weight
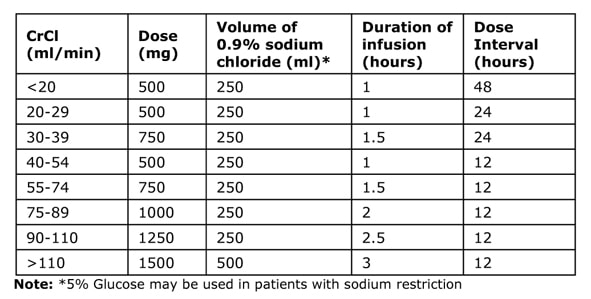
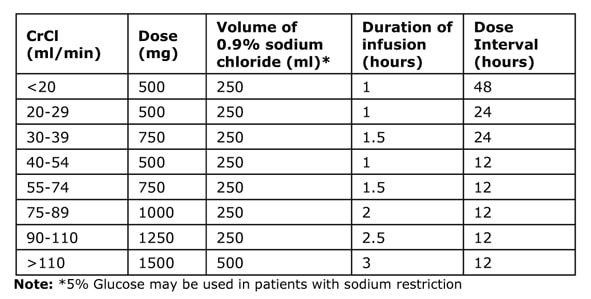
Dosing Regimen Step 2: Give the Maintenance Dose
The dose and frequency is based on the Cockcroft Gault equation (see below) for Calculated Creatinine Clearance (CrCl). Dose Intervals are either 12, 24 or 48 hours after the Loading Dose.
The dose and frequency is based on the Cockcroft Gault equation (see below) for Calculated Creatinine Clearance (CrCl). Dose Intervals are either 12, 24 or 48 hours after the Loading Dose.
The CrCl MUST be used not the creatinine value as the creatinine value does not give an accurate reflection of renal function on its own
Dosing Regimen Step 3: Measure the Trough Level
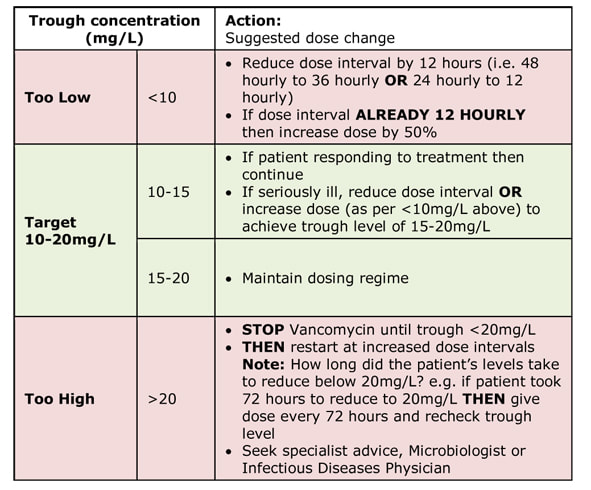
A trough level should be taken within 48 hours of starting treatment (e.g. just before the 4th maintenance dose if on 12 hourly dose interval or just before the 1st maintenance dose if on 48 hourly dose interval), THEN at least every 3 days if stable renal function, to reach the target 10-20mg/L (15-20mg/L in severe or deep-seated infections).
REMEMBER in changing renal function take trough levels more frequently (i.e. just before every dose).
A trough level should be taken within 48 hours of starting treatment (e.g. just before the 4th maintenance dose if on 12 hourly dose interval or just before the 1st maintenance dose if on 48 hourly dose interval), THEN at least every 3 days if stable renal function, to reach the target 10-20mg/L (15-20mg/L in severe or deep-seated infections).
REMEMBER in changing renal function take trough levels more frequently (i.e. just before every dose).
Teicoplanin
- Levels are not normally required unless patient is on high doses (>400mg)
- If trough too high = patient is unable to eliminate antibiotic quickly enough therefore increase the time between doses usually in 12 or 24 hour blocks of time (Graph C, Diagrammatic Interpretation of TDM)
- In severe renal failure check levels daily and redose when target level achieved
- Occasionally it is necessary to reduce the dose in order to avoid too frequent dosing but this should be discussed with a Microbiologist beforehand
Chloramphenicol
- Peak level (post-dose) in general assesses whether a therapeutic level has been achieved
- If peak too high = dose too high therefore reduce dose by approximately 10% (Graph B, Diagrammatic Interpretation of TDM)
- Trough level (pre-dose) in general assesses whether toxic levels are accumulating
Itraconazole, Posaconazole, Voriconazole and Isavuconazole
- Trough level (pre-dose) assesses whether both therapeutic levels are achieved or toxic levels are accumulating; usual practice is to adjust the dose before adjusting the frequency of dosing for antifungals as these are usually once a day dosing regimens and giving as fractions of days is problematic
- If trough too high: dose is usually too high therefore reduce dose by approximately 10% (Graph B, Diagrammatic Interpretation of TDM)

Topics in Antibiotics:
All these topics are covered in the book...Ready to buy your copy? Click here to buy your copy of "Microbiology Nuts & Bolts" Its updated and amazingly only slightly larger considering its got 1/3 more in it! (11cmx18cmx2.5cm).
- Antimicrobial Stewardship
- How Antibiotics Work - Mechanisms of Action
- How to Choose an Antibiotic
- Prophylaxis vs. Treatment
- How to Prescribe an Antibiotic
- The Daily Review of Antibiotic Therapy
- Reasons for Failing Antibiotic Therapy
- Intravenous to Oral Switching of Antibiotics
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM)
- Interpretation of TDM
- Antibiotic Dosing in Adult Renal Impairment
- Adjustment of Antibiotic Doses in Adult Renal Impairment
- Antibiotic Dosing in Obesity
- What is Antibiotic Resistance?
- How Resistance Occurs - Mechanisms of Resistance
- How is Antibiotic Resistance Spread?
- How is Antibiotic Resistance Detected in the Laboratory?
- Table of Antibiotic Spectrum of Activity
- Table of Antibiotic Tissue Penetration
- Allergy to Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
- Including pages on each: Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems and Aztreonam, Trimethoprim and Co-Trimoxazole (Septrin), Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin and Clindamycin, Gentamicin, Amikacin and Tobramycin, Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin, Vancomycin and Teicoplanin, Daptomycin, Metronidazole, Doxycycline, Tigecycline and Tetracycline, Linezoli, Rifampicin, Fusidic Acid, Colistin, Chloramphenicol, Nitrofurantoin, Fidaxomicin, Fosfomycin, Antimycobacterials, Antifungals and Antivirals
All these topics are covered in the book...Ready to buy your copy? Click here to buy your copy of "Microbiology Nuts & Bolts" Its updated and amazingly only slightly larger considering its got 1/3 more in it! (11cmx18cmx2.5cm).